 Multiple lines of text
Multiple lines of text
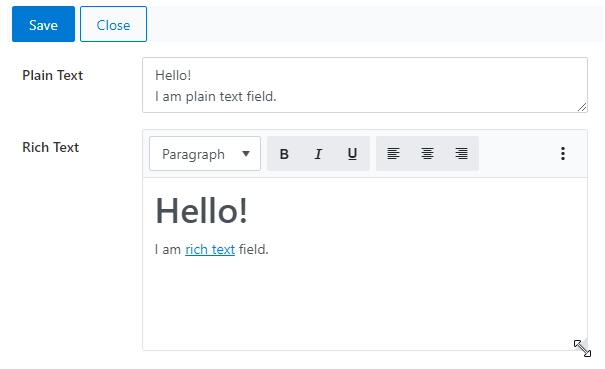
The Multiple lines of text field is used to store multiple lines of text. With the Append Changes to Existing Text setting, it can be used to store multiple versions of text.
This page contains a detailed description of the field properties and JavaScript samples which you can use with this field.
Common Properties
SharePoint Field |
General |
Title |
Control |
|---|---|---|---|
JavaScript framework
In this section, you can find basic examples of how to work with the SharePoint fields using JavaScript.
For more examples, check out Working with form fields in JavaScript article. If you are not familiar with the JavaScript framework, get started with the JavaScript basics.
Note
The field is only accessible once the form is rendered, so all calls to the field must be inside fd.spRendered event:
fd.spRendered(() => {
// make field required
fd.field('Field1').required = true;
});
Get or set field value
Access and change field value with the following property:
// get field value let text = fd.field('Field1').value; // set field value for Plain text, use \n to start new line fd.field('Field1').value = 'Some text \nNew line of text'; // set field value for Rich text, use HTML formatting fd.field('Field1').value = 'Tenerife is the largest of the eight <a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Canary_Islands" rel="nofollow">Canary Islands</a>.';
Handle change event
Execute a function when a field value has been changed:
fd.field('Field1').$on('change', value => { // log new value to browser's console console.log(value); });
Make field required
Make a field required or optional:
// make field required fd.field('Field1').required = true; // make field not required fd.field('Field1').required = false;
Disable field
Make a field non-editable. The field value can still be changed with JavaScript and saved:
// disabled field fd.field('Field1').disabled = true; // enable field fd.field('Field1').disabled = false;
Get HTML element
Access HTML element inside the field in order to modify it, hide it, or do something else.
// access field's control let htmlElement = fd.field('Field1').$el; // access field's block, which includes title and control let htmlParentElement = fd.field('Field1').$parent.$el;
Hide field
Hide a field from a user. The field value can still be accessed and changed with JavaScript.
// hide field fd.field('Field1').hidden = true; // show field fd.field('Field1').hidden = false;
Clear field
Clear field value.
fd.field('Field1').clear();
Configure widget
You can access the widget used by the field in Rich text mode. The widget is based on Kendo UI Editor.
// get the widget fd.field('Field1').widget; // change the widget's configuration fd.field('Field1').widgetOptions = { placeholder: 'Enter your text here' };
widgetOptions is the same as widget.setOptions({}) but can be defined before widget initialization.
Customize toolbar
The property contains settings for Kendo UI MultilineTextBox control and is applicable for Rich text fields only. Customize the collection of tools that are used to interact with the text. Tools may be switched on by specifying their names.
The available editor commands are:
Basic text formatting:
‘bold’
‘italic’
‘underline’
‘strikethrough’
‘subscript’
‘superscript’
Font and color:
‘fontName’
‘fontSize’
‘foreColor’
‘backColor’
Alignment:
‘justifyLeft’
‘justifyCenter’
‘justifyRight’
‘justifyFull’
Lists:
‘insertUnorderedList’
‘insertOrderedList’
‘indent’
‘outdent’
Links, images and files:
‘createLink’
‘unlink’
‘insertImage’
‘insertFile’
Table editing:
‘tableWizard’
‘createTable’
‘addColumnLeft’
‘addColumnRight’,
‘addRowAbove’
‘addRowBelow’
‘deleteRow’
‘deleteColumn’
Structural markup and styles:
‘formatting’
‘cleanFormatting’
HTML code view:
‘viewHtml’
Print edited field:
‘print’
Custom:
Add a custom button to the tools pane which will run the JavaScript function.
Example:
fd.spRendered(() => {
fd.field('Field1').ready(field => {
field.widgetOptions = {
tools: [
{ name: 'italic' },
{ name: 'underline' },
{ name: 'justifyLeft' },
{ name: 'justifyCenter' },
{ name: 'justifyRight' },
{
name: 'custom',
tooltip: 'Insert profile template',
exec: function(e) {
let editor = $(this).data('kendoEditor');
editor.exec('inserthtml', {
value: '<strong>Name: </strong><br/><strong>Age: </strong><br/><strong>Gender: </strong><br/><strong>Email: </strong><br />'
});
}
}
]
}
});
});