Getting started
User guide
- Settings
- Form sets
- Containers
- Controls
- SharePoint fields
- Common fields
- JavaScript
- CSS
- Display mode: panel, dialog, fullscreen
- SharePoint web parts
- Microsoft Teams tab
- Forms versioning
Provisioning forms
- Provisioning setup
- Provisioning API
- Provisioning forms (samples)
- Provisioning Form sets and display settings (samples)
General
- YouTube
- Licensing
- Manage subscription
- Billing and payments
- Privacy policy
- Data protection and security
- Version history (Microsoft 365)
- Version history (SharePoint 2019/SE)
Multilingual support
Navigation between forms
Generating PDF documents
- Save SharePoint form as PDF
- Generate PDF from DOCX template with Plumsail Documents
- Generate PDF from DOCX template with Word Online (Business)
Power Automate
How to design complex and responsive forms with grids in SharePoint Forms
Grid is a flexible container. It allows you to place fields and controls side by side, and control how many columns each row has. It’s used as a basis on every form and inside other containers such as Tab Control, Accordion, and Wizard. Our Grid is based on Bootstrap Grid.
In this article, we describe the advantages of using Grids instead of Tables in Forms.
Key advantages
Responsiveness – an ability to design a single layout that is adjusted to any screen size automatically. It makes Grid even more useful when designing mobile-friendly forms.
Flexibility – no need to define the number columns for the whole Grid unlike we do for Tables. Each row can contain an arbitrary and unique number of columns. Thus, you can create a pretty complex form by using just a single Grid. The generated code is more compact with Grids and thus is rendered much faster by browsers.
Powerfulness – since the Grid is based on very popular Bootstrap grid, it contains a lot of built-in features e.g. predefined classes for adjusting forms to different screen sizes, aligning content inside a Grid, configuring spacing between cells, etc.
Basics of Grid
Plumsail Forms leverages the Bootstrap grid providing a series of containers, rows, and columns to layout and align content in forms. It is built on flexbox and is fully responsive.
Each row can be split into up to 12 columns. In most cases, you will not use all 12 individual columns. But 12 evenly divides into 6 (halves), 4 (quarters) and 3 (thirds) that gives you a wide range of possibilities to organize content in a form.

Limit of 12
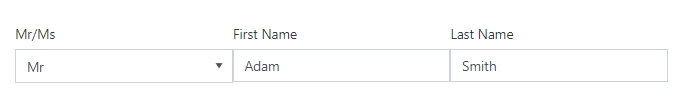
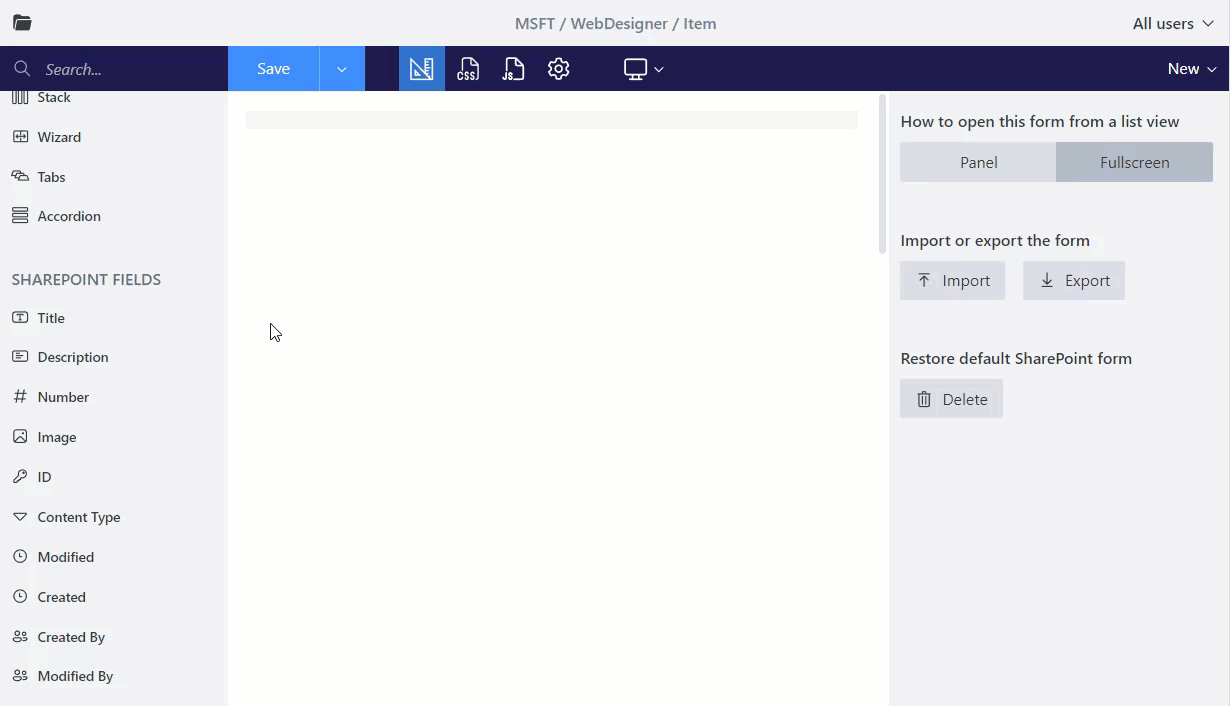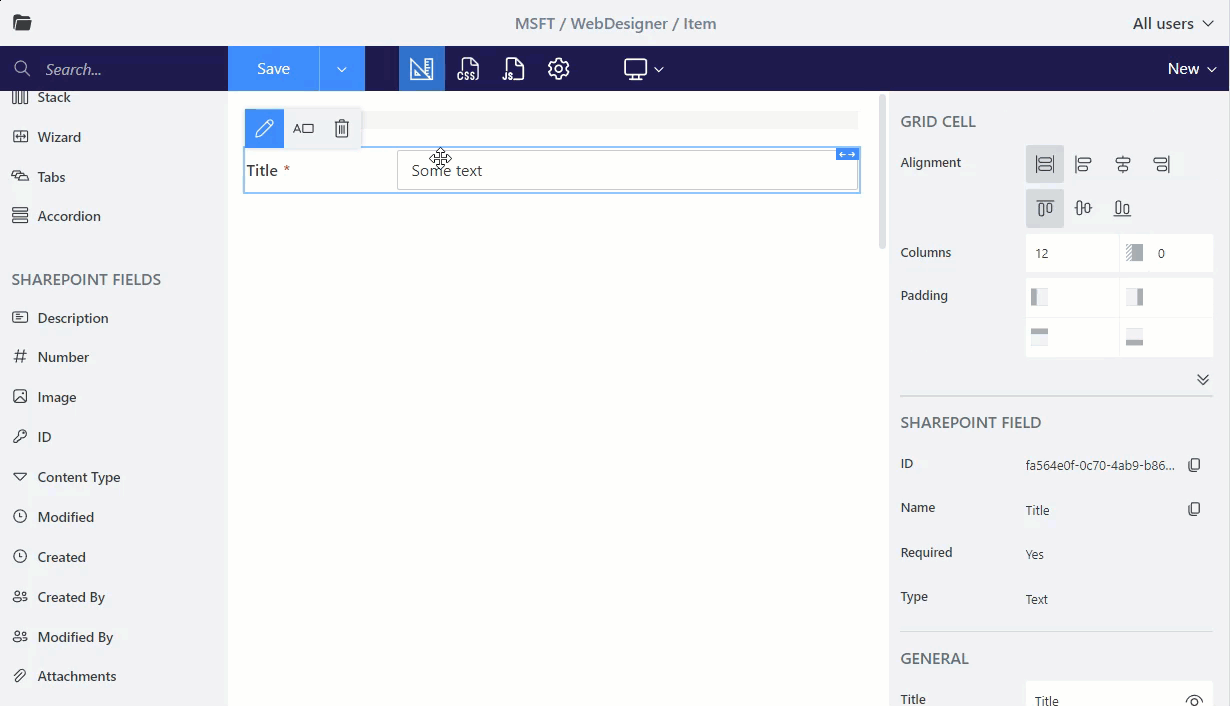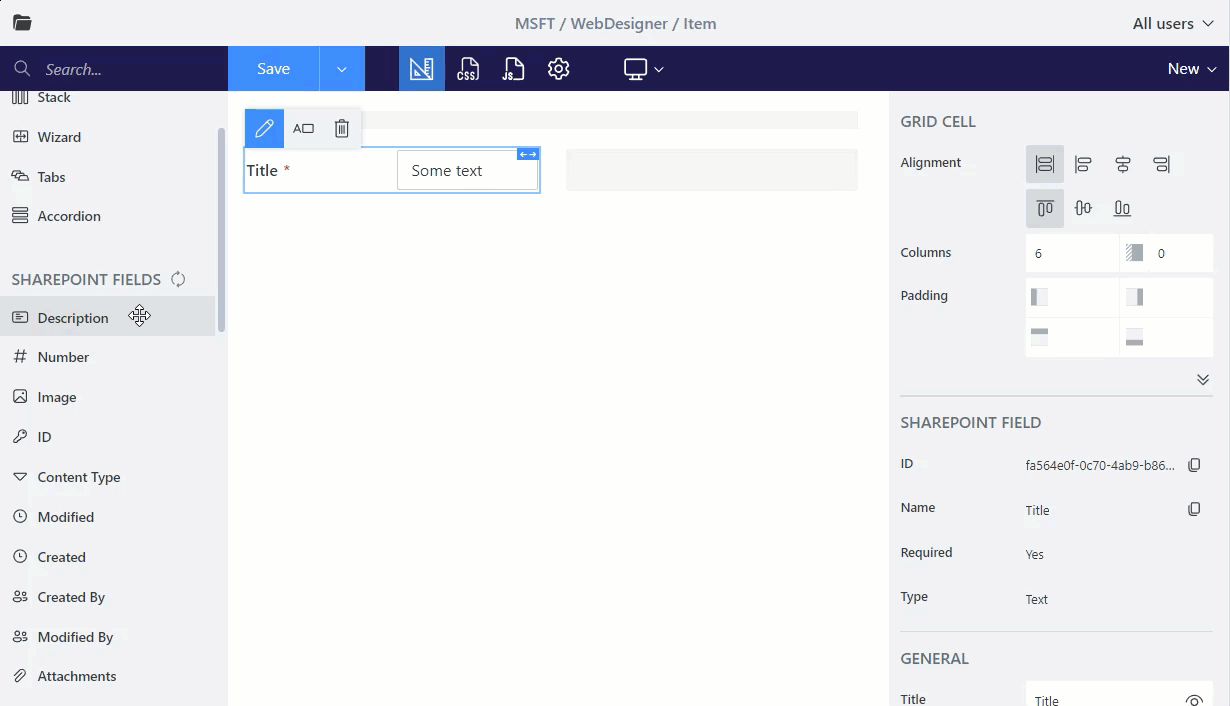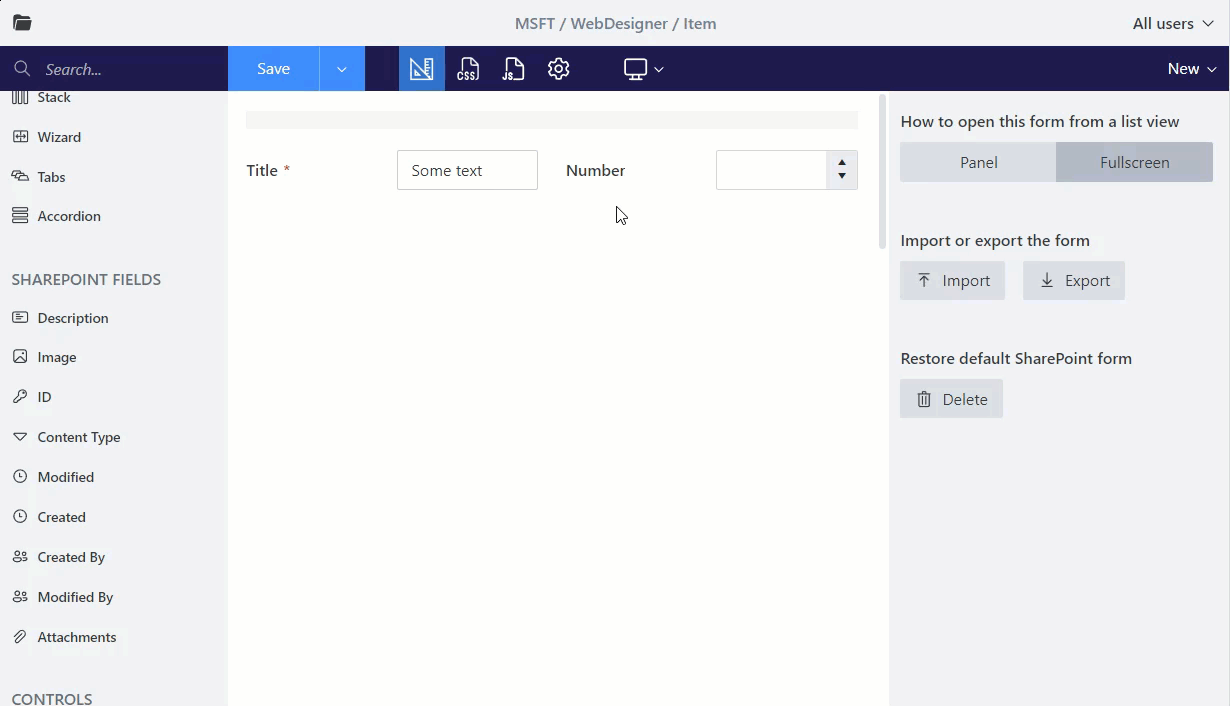
By default, each field or control placed into a form takes 12 columns of the Grid. Change the width of the Grid cell to place the fields in a row next to each other:
Title width
Standard Field title’s width is 120px, but you can adjust it to better fit form’s layout:
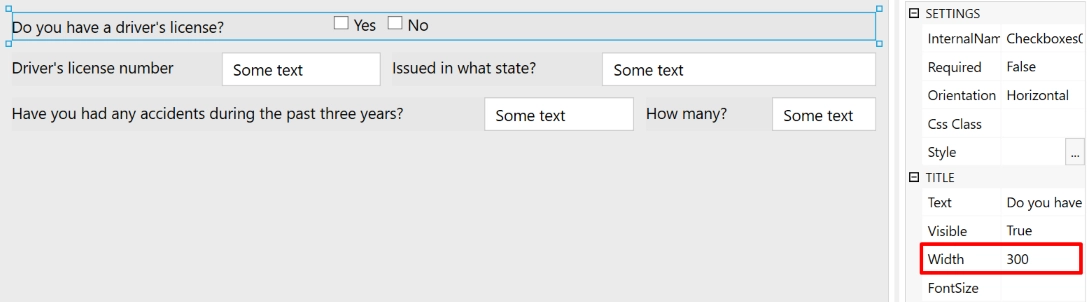
Nested Grid
You don’t need to limit yourself with 12 columns – nested Grids will allow you to adjust the placement of the fields exactly like you want to. Nested Grids also provide you an opportunity to place some vertically organized fields in a single row.
There are a lot of scenarios that require organizing fields in multiple rows in a single row of a parent Grid. Here, the nested Grids come in handy. In this example, we’ve added the Grid container to the form and placed fields inside in two rows:
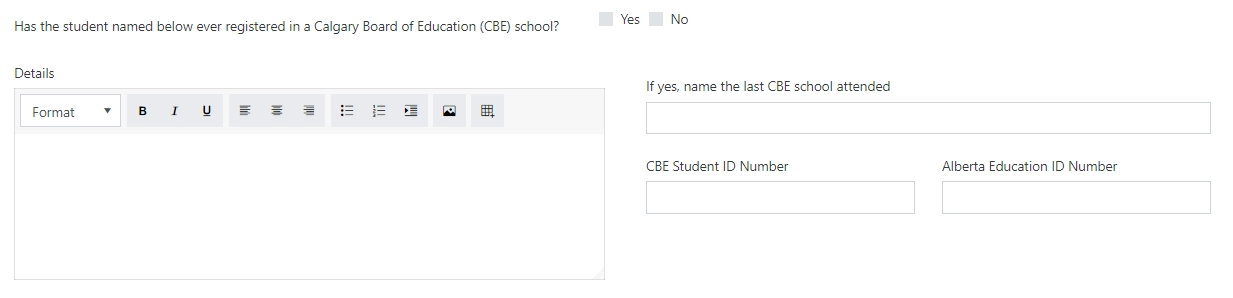
Note
Another example for nested grids combining fixed and flexible layout can be found in the horizontal alignment with Stack container section.
Offset
You can easily add spacing between fields or a field and Grid border with the Parent Grid’s Offset property.
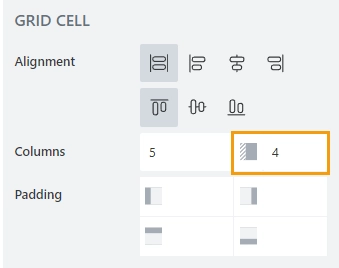
That’s how it looks like:
Stacked property and advanced responsiveness
In addition to the concept of column width, Bootstrap has different breakpoints or grid sizes. Each grid size encompasses a range that is designed to best-fit typical device screen widths such as that of desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. These grid sizes enable you to change the layout of columns to best match different screen widths and device.
Designer implements the breakpoints functionality with Stacked property.
To make the Grid more responsive, Stacked property has four screen sizes on which the columns are stacked: Never (<576 px), Small (>=576px), Medium (>=768px), Large (>=992px). For example, if the Stacked property is set to Small, the columns will be stacked at the size of the screen < 576 px. If the Stacked property is set to Never the columns will not be stacked at all.
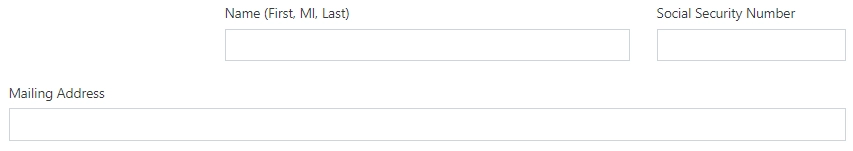
By default, the Stacked property of the Parent Grid is set to Small. That means that fields are not stacked on larger screens:

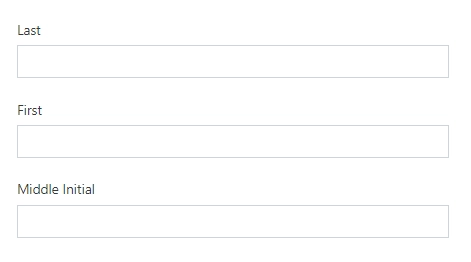
But they will be stacked for the screens with size less than 576 px:
The Stacked property of the root Grid cannot be changed, but you can override it in a nested Grid:
By combining different values of the Stacked property for nested grids, you can define how your form will be adjusted to different screen sizes.
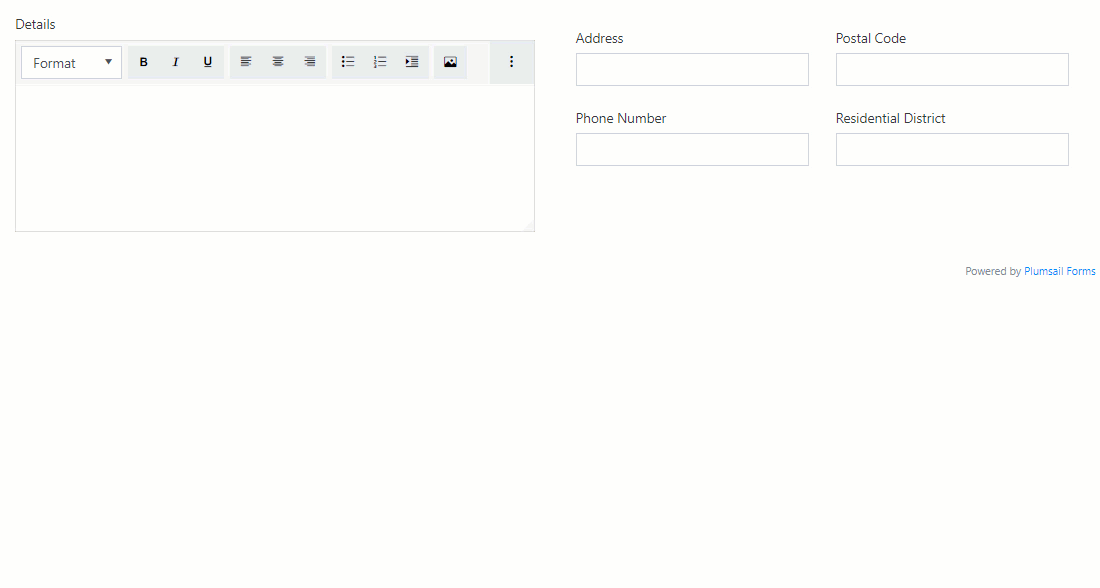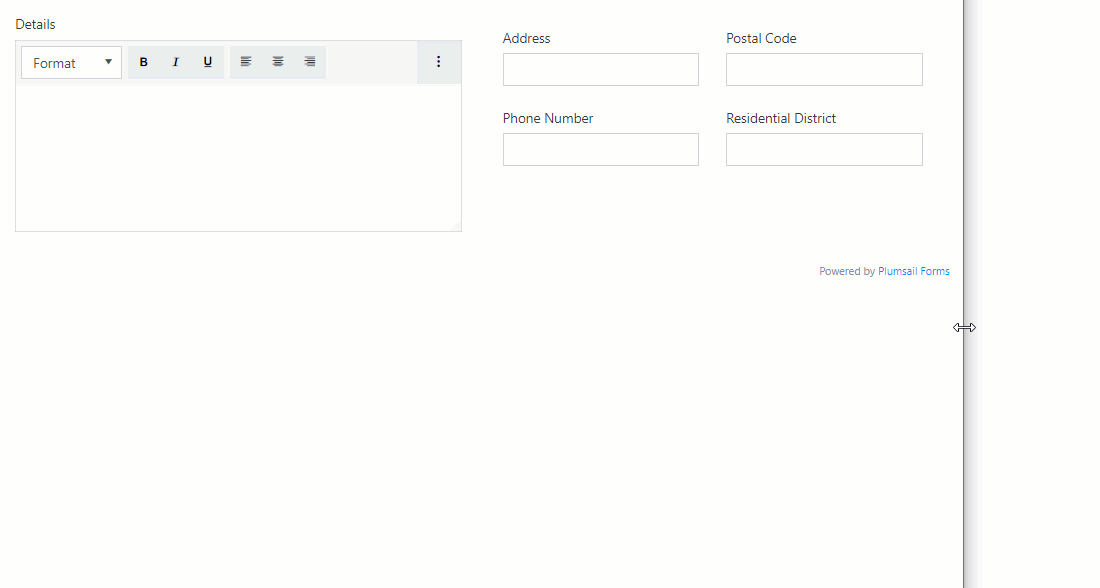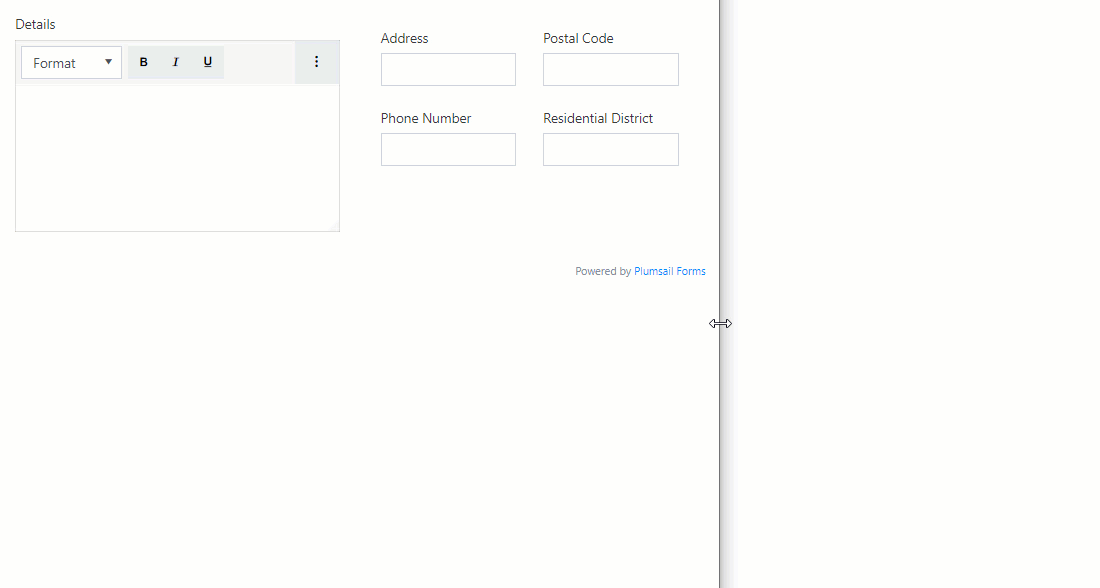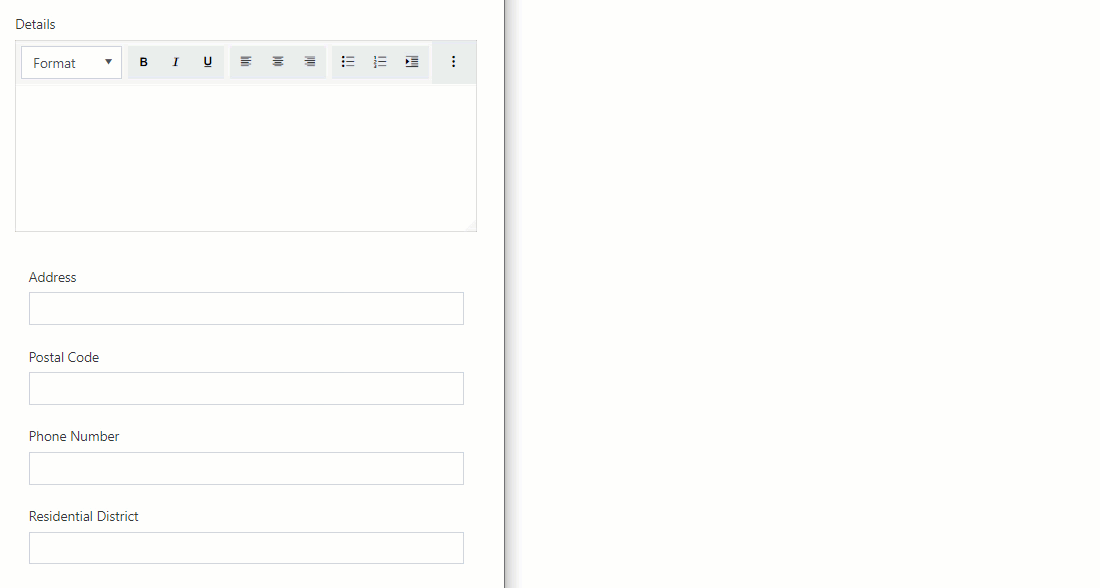
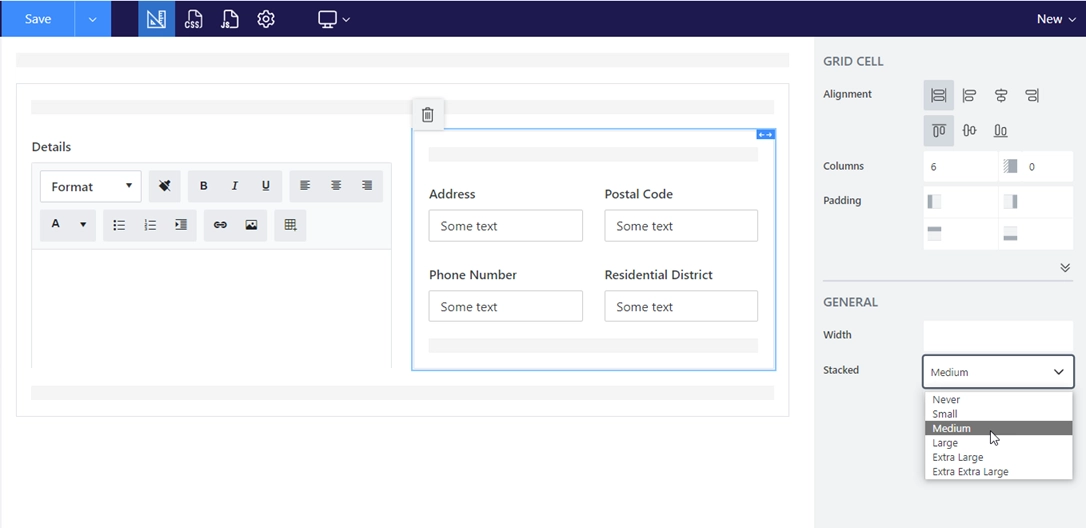
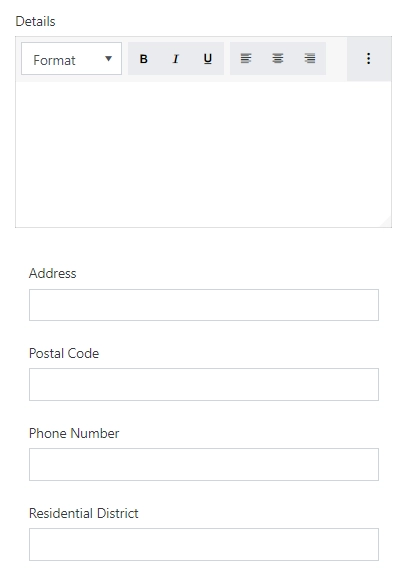
Example form
In the form below, I want to leave the Details field alone in a row even for a medium screen size while the remaining fields should be moved to a separate row as a table and collapse into a single column for a small screen.
For this purpose, I’ve added a Grid and set its Stacked property to Large:
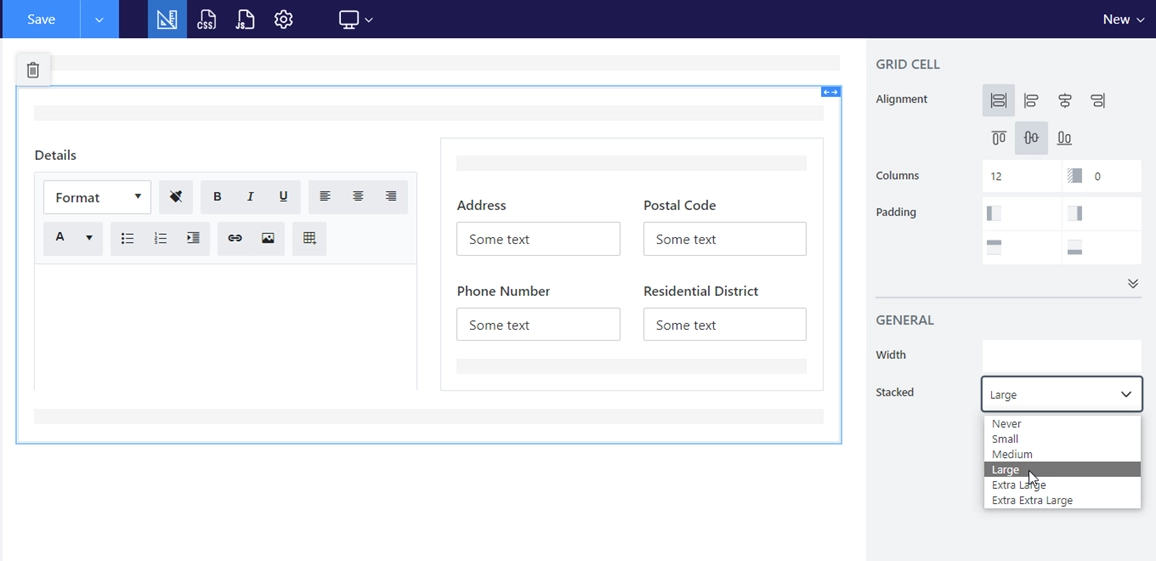
Then, I’ve added a nested Grid for Address, Postal Code, Phone Number and Residential District and set its Stacked property to Small which is default.
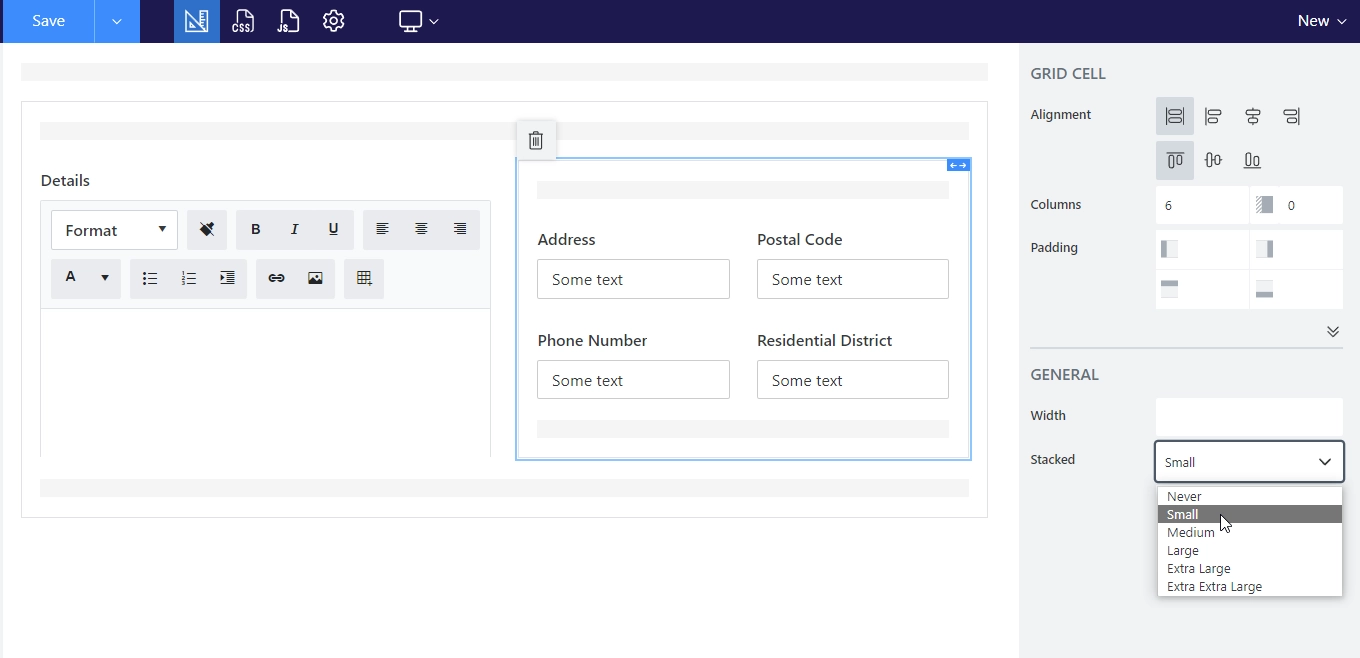
PC Screen
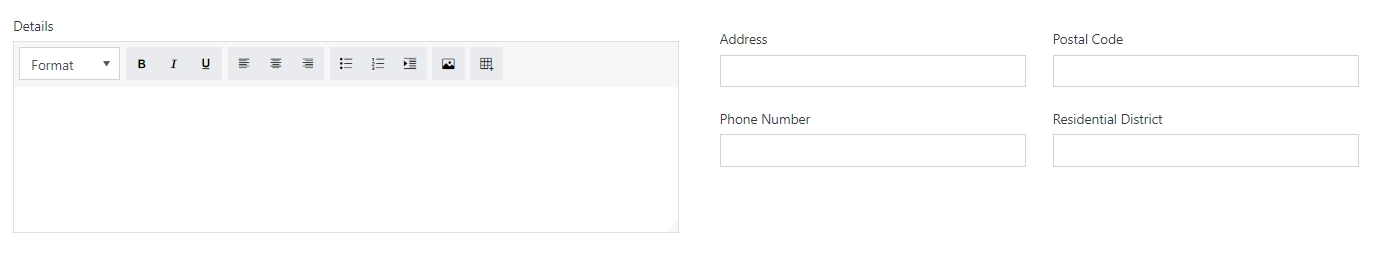
Tablet Screen
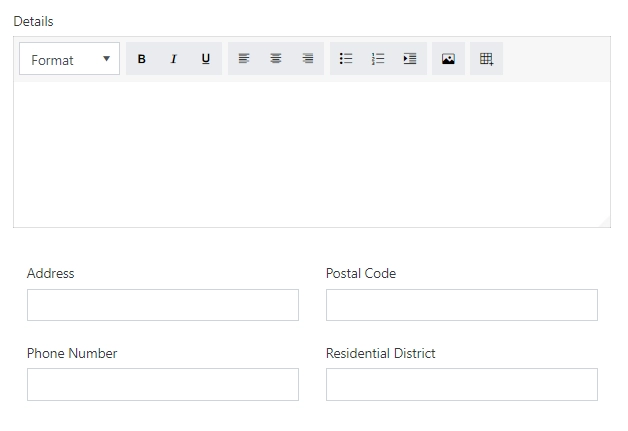
Mobile Screen
Combining Stacked property with extra CSS-classes provided by Bootstrap e.g. col-sm-, col-md-, or col-auto, allows you to define a layout of any complexity which perfectly suits any screen size.
Alignment
Determines how to align elements inside the grid cell by changing the Alignment property. You can align elements vertically and horizontally.
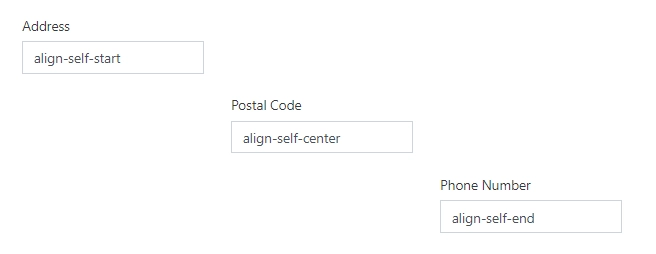
Vertical alignment
You can align elements to the top, center, or bottom of the Grid cell:

That’s the example of the verticall alignment:
Horizontal alignment
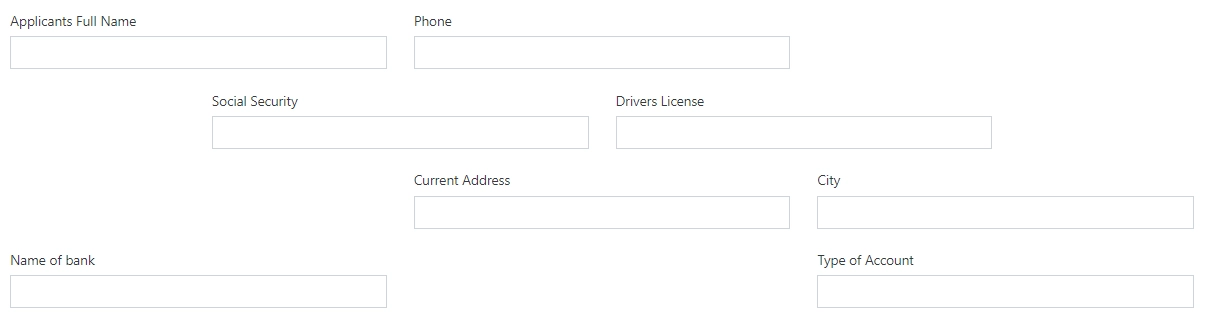
You can align elements horizontally. Choose from between, start, center or end.

Here’s the example, each row uses different option for horizontal alignment:
Horizontal alignment with Stack container
If you combine Grid with Stack container, you can have horizontal alignment where some elements are fixed size in pixels, and others scale with the screen. For example, in the following case, the left column with personal information is fixed, and the last column with the message is filling out the rest of the screen:
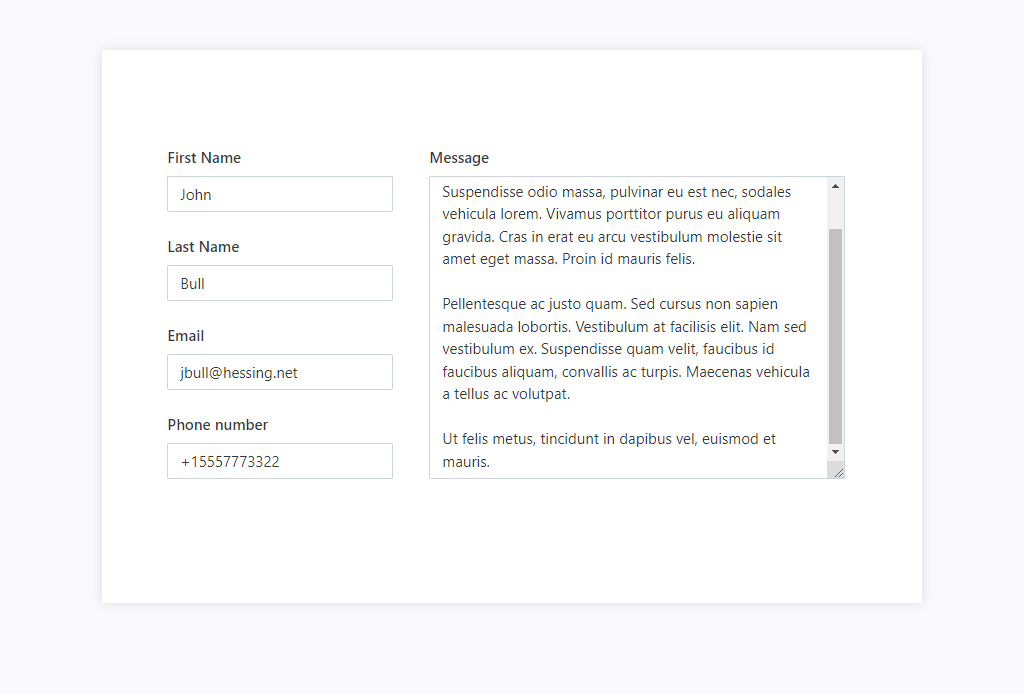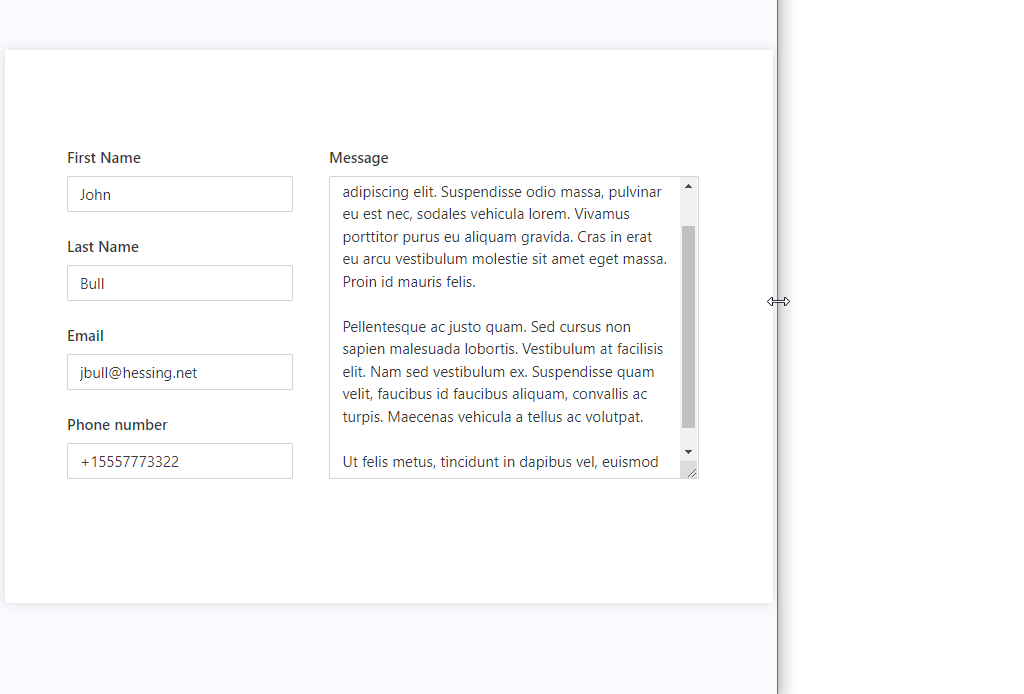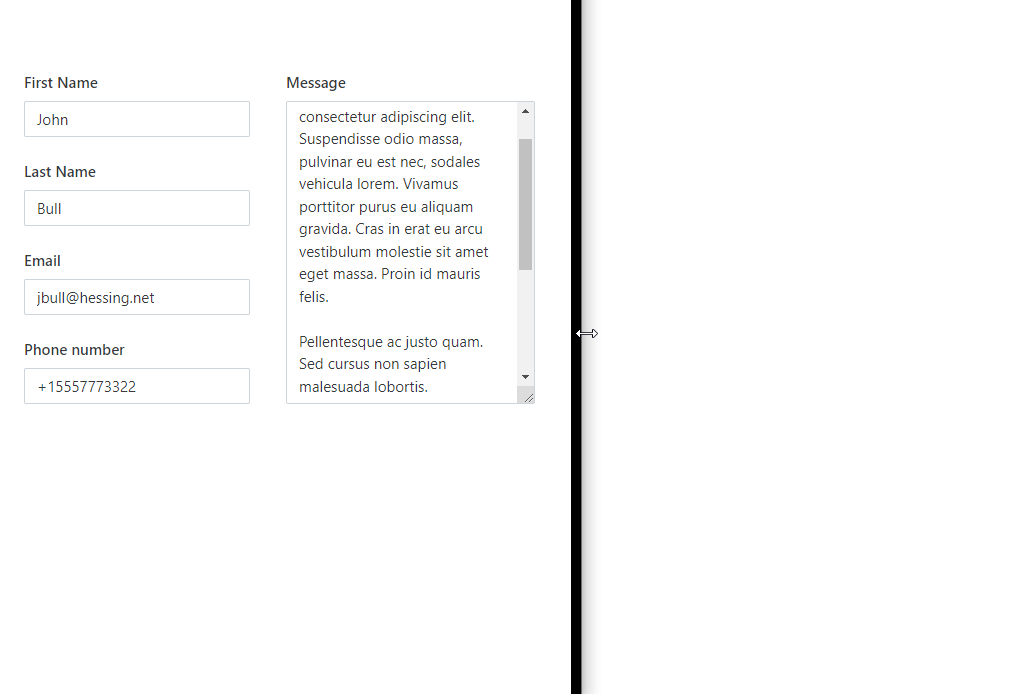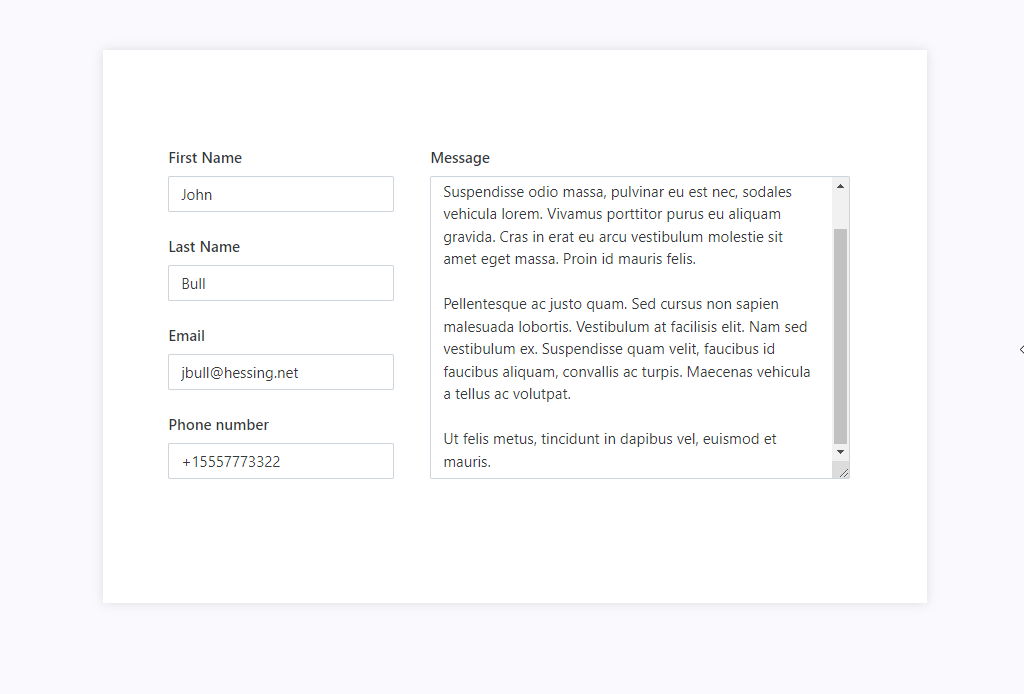
This is achieved by using nested Grids and Fill property of the Stack container:
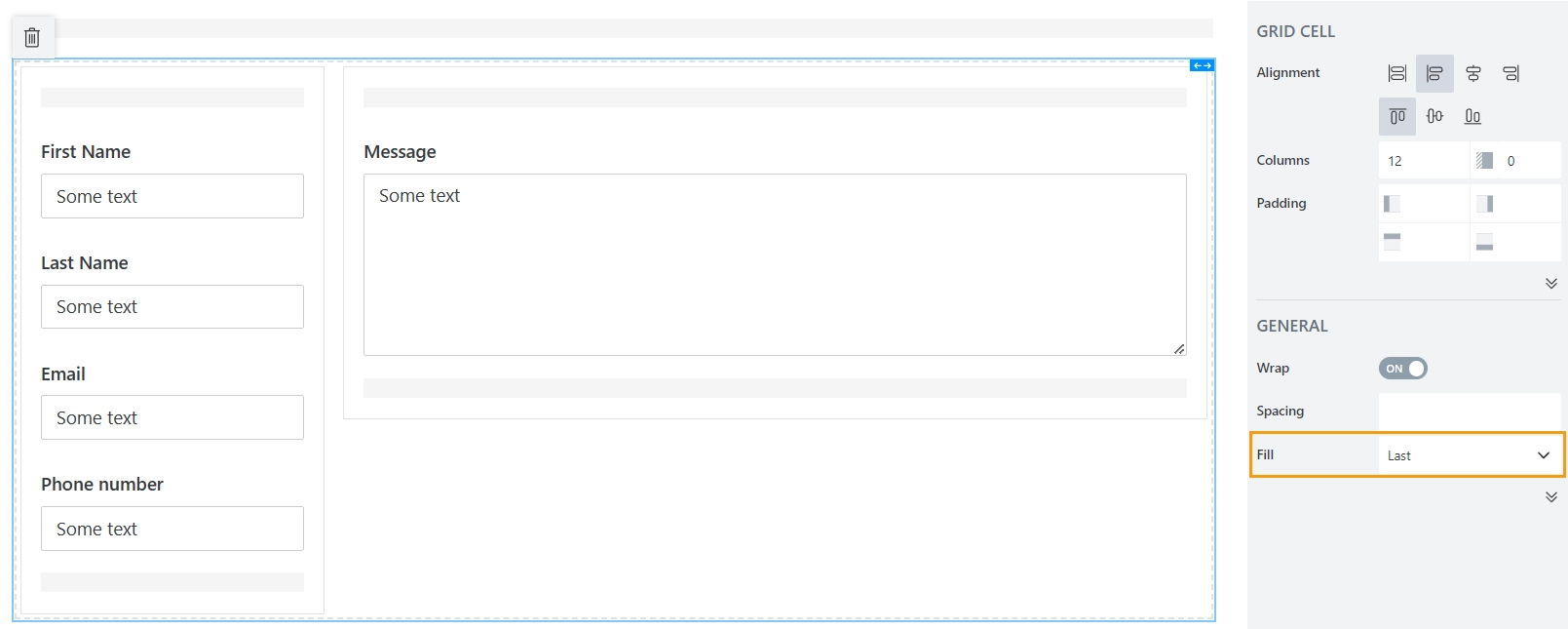
No spacing
The spacing between columns can be removed with no-gutters CSS class.
Code sample:
fd.spRendered(() => {
$('.custom-grid').find('.row:not(.form-group)').eq(0).addClass('g-0');
});