 Tabs
Tabs
The Tabs container organizes form content into tabs.
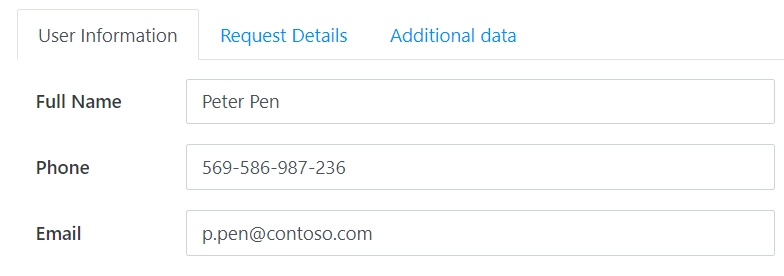
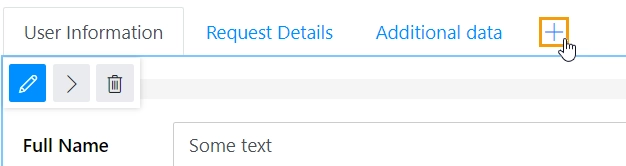
You can add as many tabs as you need. To add a new tab, simply click on the plus symbol:
This page contains a detailed description of the container properties and JavaScript samples that you can use with this container.
Properties
Here you can find properties specifically related to the Tabs container.
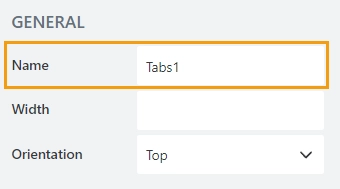
Name
A unique identifier for the container.
JavaScript
The Name property allows to work with the container via JavaScript code, like this:
fd.rendered(() => {
// hide container
fd.container('TabControl1').hidden = true;
});
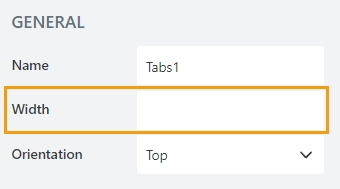
Width
The property defines the width of the container in pixels.
If left blank, the container takes up the entire available width in the current grid cell.
Position
The property defines tabs position relative to the content inside:
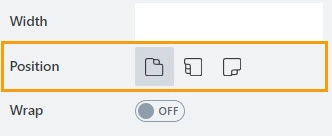
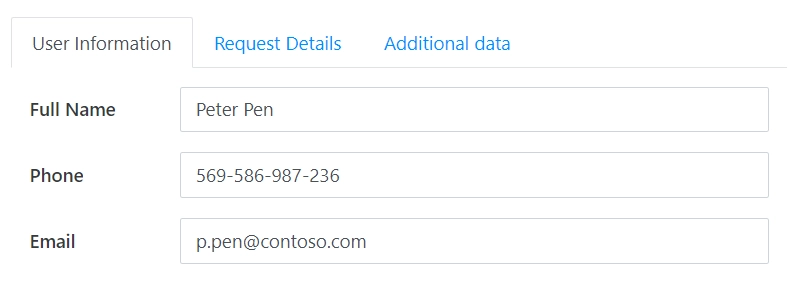
Tabs can be positioned at:
Top:
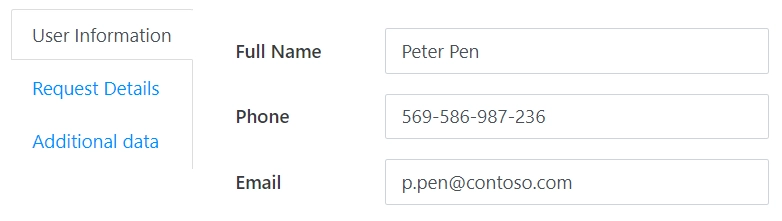
Left:
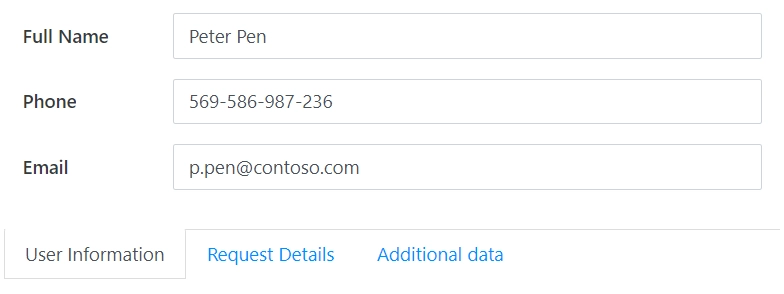
Bottom:
Pills
The property defines the appearance of the container’s navigation:
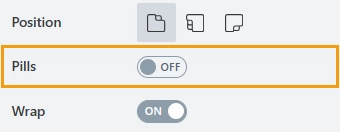
disabled: the navigation appears as tabs:
enabled: the navigation appears as pills:
Wrap
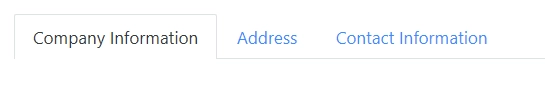
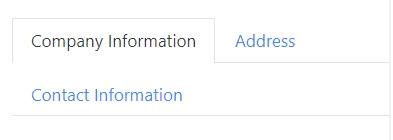
The property defines how tabs behave when the container exceeds the window width.
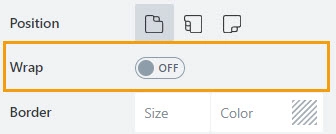
disabled: users will see arrows for navigating between tabs:
enabled: tabs will wrap onto multiple lines:
Border
The property defines the tabs’ border width and color:

Frame
The property defines the horizontal and vertical padding (extra space) and border radius (roundness) of the tabs:

Fill
The property defines the background color of the tabs:
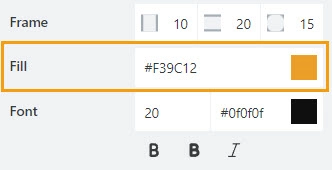
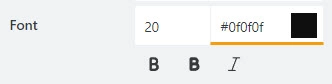
Font
Format tabs’ titles using these settings:
font size:
font color; use the color picker or enter the Hex color code:
font style: Normal, Bold or Italic:
Tab title
The property defines the header of a tab.
JavaScript framework
In this section, you can find basic examples of how to work with the containers using JavaScript.
If you are not familiar with the JavaScript framework, get started with the JavaScript basics.
Note
The container is only accessible once the form is rendered, so all calls to the containers must be inside fd.rendered event:
fd.rendered(() => {
// hide the container
fd.container('Container1').hidden = true;
// show the container
fd.container('Container1').hidden = false;
});
Get HTML element
Access HTML element inside the container.
// access container's HTML let htmlcontainer = fd.container('Container1').$el;
Hide container
Hide a container from a user.
// hide container fd.container('Container1').hidden = true; // show container fd.container('Container1').hidden = false;
Tabs
The property holds tabs of the container as an array of objects. Can be used to get tabs and their properties.
fd.container('Container1').tabs
Detect tab change
Execute a function when a user switches between tabs:
fd.container('Container1').$watch('currentTab', (newIndex, prevIndex) => {
alert('Previous tab: ' + prevIndex);
alert('Current tab: ' + newIndex);
});
Disable tab
Disable or enable a tab:
// disable the second tab
fd.container('Container1').tabs[1].disabled = true;
// enable the second tab
fd.container('Container1').tabs[1].disabled = false;
Hide tab
Hide or show a tab dynamically using a combination of JavaScript code and CSS.
Disable the tab:
// disable the second tab
fd.container('Container1').tabs[1].disabled = true;
// enable the second tab
fd.container('Container1').tabs[1].disabled = false;
Add CSS styling to hide the disabled tab:
.fd-form .tabset .disabled{
display: none; /* hide disabled tabs */
}
Highlight tab
Highlight specific tab using CSS:
/* set the second tab background */
.fd-form .tabset li:nth-child(2) a {
background-color: crimson !important;
color: white !important;
}
/* set the second tab background when it is opened */
.fd-form .tabset li:nth-child(2) a.active {
background-color: gold !important;
color: black !important;
}
Current tab
Get the index of the currently opened tab:
// returns integer
fd.container('Container1').currentTab;
Next/Previous tab
Open the next or previous tab:
// open next tab
fd.container('Container1').nextTab();
// open previous tab
fd.container('Container1').previousTab();
Open tab
Open a tab by index:
// open the first tab
fd.container('Container1').setTab(0);
// oepn the last tab
fd.container('Container1').setTab(
fd.container('Container1').tabs.length -1
);
Tabs orientation
Get or set tabs position:
// returns the current tabs position
fd.container('Container1').orientation;
// set tabs position
fd.container('Container1').orientation = 'left';