JavaScript editor and global variables
Use the JavaScript editor to customize the JavaScript for the entire form:
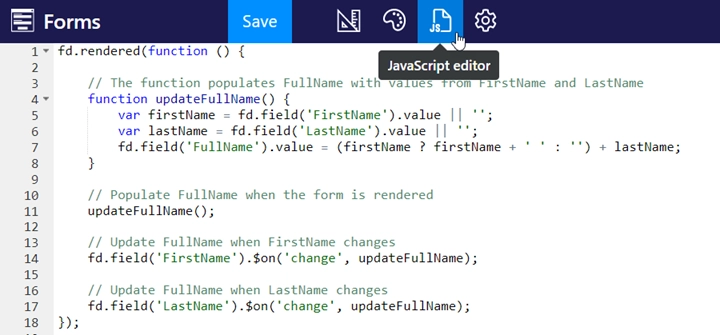
The code entered in the editor is executed after the form is loaded.
The following predefined global variables can be used directly from the JavaScript editor:
fd
fd is a Form Manager that provides access to all events, containers, controls, fields, validators, and data of the form.
Whenever you want to manipulate your form, you must call the manager first.
// the form is ready
fd.rendered(() => {
// and its fields are available to get/set
fd.field('Title').value = 'New Title';
});
Note
fd is accessible globally on the Preview page, so you can run tests directly from the browser console (F12).
$
$ allows you to access jQuery library. It can be used to apply direct changes to DOM, hide and show fields, and much more.
// hide fields by CSS class
$('.field-to-hide').hide();
// change input background color
$(fd.field('Field1').$el).find('input').css('background-color', 'red');
Vue
Vue is a global Vue object. Allows you to register global components or wait for the next DOM update cycle with Vue.nextTick.