Getting started
- Design forms
- Share forms
- Manage users
- Collect form data
- Configure notifications
- Handle form data in Power Automate
- Handle form data in Make
- Handle form data in Zapier
- Handle form data with REST API
- Connect to Airtable
- Connect to SharePoint
User guide
General
- YouTube
- Licensing
- Manage subscription
- Billing and payments
- Privacy policy
- Data protection and security
- Version history
Integrations
Multilingual support
Provisioning public forms with NuGet package
SharePoint field properties
This article describes common properties available to all supported fields, which you can edit in the designer, but also shows how the same properties can be used dynamically with JavaScript.
SharePoint Field
The properties in this section are read-only. Some properties can be modified in the SharePoint column settings.
Id
A unique identifier of the SahrePoint column. Can’t be modified.

Name
The internal name of the SharePoint column.

JavaScript
The Name property allows to work with the field via JavaScript code, like this:
fd.rendered(() => {
// can access the field using its Name:
fd.field('Title').value = 'Project Delta';
});
Important
The Internal name can’t be changed. You can only change the display name of the column.
Required
Indicates whether the field is required.
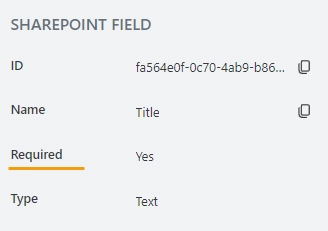
You can change this property in the SharePoint column settings:
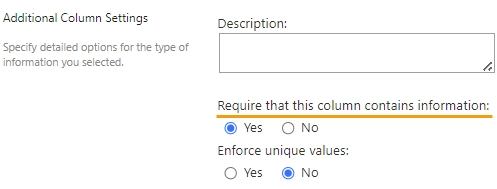
Or using the JavaScript:
// returns the field's required status as true/false fd.field('Text1').required; // sets the field's required status fd.field('Text1').required = true;
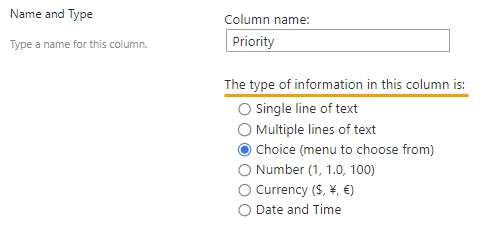
Type
Indicates the column type.
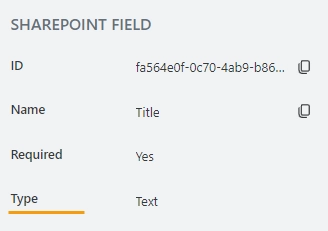
You can change the column type in the SharePoint column settings:
General
Title
Specify text of the title that will appear next to the field.
JavaScript
This code will allow you to get or set the field’s title dynamically:
// returns the field's title as a string
fd.field('Field1').title;
// sets the field's title
fd.field('Field1').title = 'Last Name';
Toggle the visibility of the Title on/off:
Layout
Select if the title will appear to the left of the field, or right above it.
Hint
Defines a placeholder text that appears in the input before a user starts typing:
JavaScript
This code will allow you to get or set the field’s placeholder text dynamically:
// sets the field's Hint
fd.field('Field1').placeholder = 'Enter your name';
Read-only
Define whether a user can view or edit the contents of the field:
Class
Add a CSS class to the field, which comes in handy with CSS or even JavaScript code. This will work like class attribute for an HTML tag.
Same class can be applied to multiple fields, and then you can use CSS to modify the appearance of these fields. For example, here we’ve used the following CSS code in CSS editor to give fields with my-class a blue background, white text and rounded corners, with a little bit of padding:
.my-class { color: #FFFFFF; padding: 10px; background-color: #1E90FF; border-radius: 30px; }
Style
Add custom CSS style to the field. This will work like style attribute for an HTML tag.
This style will allow you to hide the field, making it invisible to user (but still usable with JavaScript):
display: none;
You can also apply different styles to it. For example, the following style will allow you to add a thin gray border around the field:
padding: 10px; border: 1px solid #CED4DA;
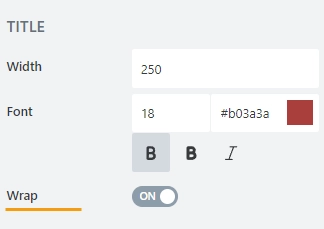
Title
Width
Specify in pixels how much space should the field’s title take.
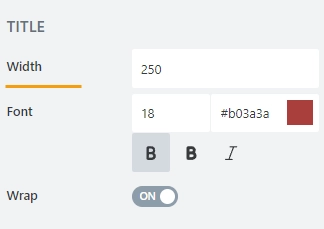
Font
Change the formatting of the field’s title using these settings:
font size:
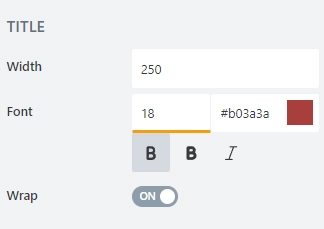
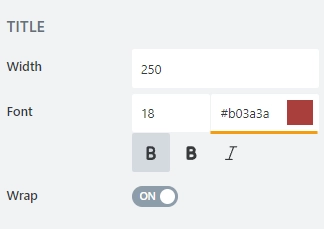
font color; use the color picker or enter the Hex color code:
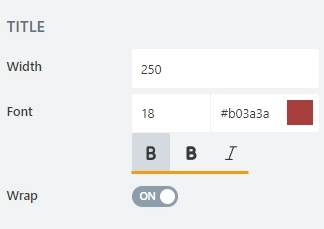
font style: Normal, Bold or Italic:
Wrap
Select if the title’s text should wrap in multiple lines when there is not enough space, or just be shortened until it fits (with dots… at the end).
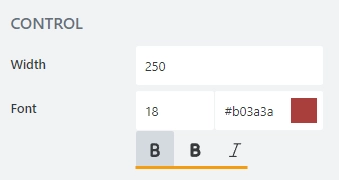
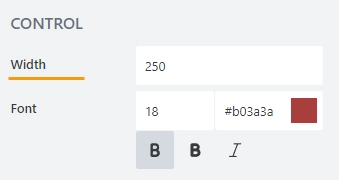
Control
Width
Specify in pixels how much space should the field’s field take.
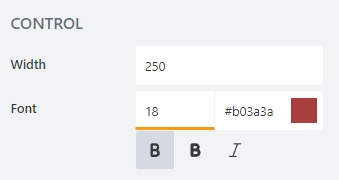
Font
Change the formatting of the field’s control using these settings:
font size:
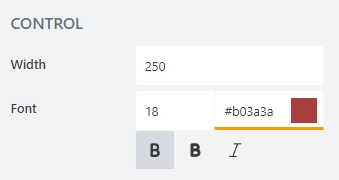
font color; use the color picker or enter the Hex color code:
font style: Normal, Bold or Italic: